Research shows that an average of $8,563.00 per Canadian is spent annually on health-related expenses. Most people in Canada are familiar with the country's healthcare system, but supplementary insurance plans also help reduce out-of-pocket costs.
In Canada, the healthcare system provides high coverage for all its citizens. However, there may be occasions when you need to pay for drugs or services, and supplementary health insurance can be helpful.
This article will help you better understand additional health insurance coverage in Canada.
An overview of the healthcare system in Canada
In Canada, Citizens, Permanent Residents, and eligible non-immigrant residents are provided access to publicly-funded, free healthcare. This healthcare system is called Medicare. This system, often called “universal health insurance” or “universal health care coverage,” is highly generous.
Canada has thirteen provinces and territories. Each is responsible for managing and financing its healthcare system. Depending on the size of the population, each region receives varying levels of financial support from the federal government. As a result, though they could be more efficient, provincial health services are generally effective.
In Canada, primary medical care is free, but this care does not include all services. For example, Canadians generally pay for dental care and prescription medications. In some cases, certain provinces and territories may provide additional coverage to special groups.
Canada's healthcare system amongst its international peers
The Commonwealth Fund Report ranks Canada's healthcare system ninth among eleven high-income countries. Taxpayers pay for Canadian Medicare, and the government health system works rather well.
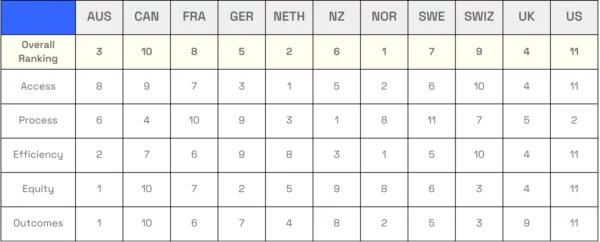
Canadians' main complaint about their healthcare system is the extended time they may wait for medical services. This wait time could be greater than that of other countries.
What is supplementary health insurance in Canada?
Supplementary health insurance provides access to medical services not covered by the public health system in Canada. These services may include specific treatments, tests, or medications including, but not limited to, the following:
- Chiropractic services.
- Dental services and hygiene.
- Massage therapy.
- Physiotherapy.
- Podiatry.
- Prescription drugs.
- Private hospital rooms.
- Eye exams and vision care.
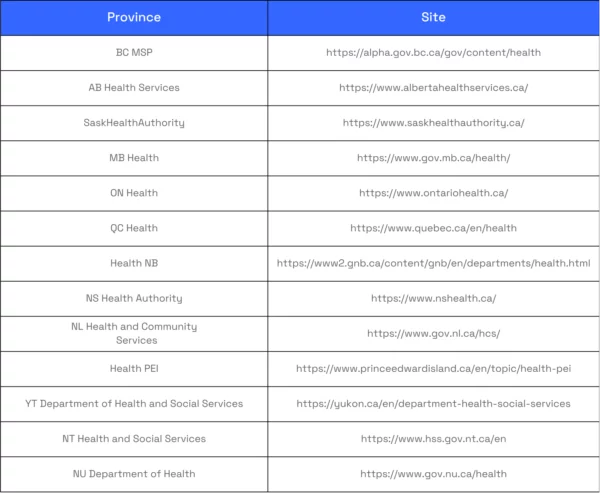
You can find more details about what supplemental health insurance covers by visiting your responsible provincial government agency's website. For example, if you are a resident of Ontario, you can go to the Financial Services Regulatory Authority of Ontario website.
The following is a complete list of all provincial and territorial health service websites in Canada.
How supplementary insurance works
Supplementary health and dental insurance operate similarly to other forms of insurance. The risk of paying for services is shared among people who contribute to a fund.
As you plan for the holidays, you should prepare for medical emergencies with health insurance. This helps to minimize the expense of any unexpected medical treatments that may be necessary.
If your job offers other health or dental plans, your employer will be responsible for paying the premiums. And you get to enjoy the benefits. This type of insurance is prevalent in Canada.
Can you buy your insurance?
For Canadians, universal healthcare cannot be replaced entirely. But you can purchase an additional health plan to cover costs not covered by the national system.
This information is for you if you have moved to Canada recently or returned after being away for a long time. You might want to purchase extra health insurance if you're not yet eligible for public health care benefits. Taking advantage of universal services usually takes three months of living in Canada.
Supplementary health insurance likely won't cover all your medical costs. You may have to pay a certain sum upfront as a service deductible (generally up to $2000.00). Or you might pay an annual deductible (usually $50-100.00).
In addition to the deductible, you may be required to pay a portion of your medical costs. This is referred to as co-insurance. You can consult your provincial guideline website to learn more about deductibles and co-insurance in your area.
Do you need supplementary insurance if you're covered through work?
The answer to this question will depend on your requirements. Understanding all the details of your employer's health insurance plan is essential.
If you have medical requirements not covered by public health or work health insurance, you may want to consider extra coverage. This could be in the form of health or dental insurance. Speak to an insurance agent to find out more information.
Group plans explained
Typically, employers offer health coverage through a group plan. However, you can also access group health insurance through a professional organization.
If you receive health insurance through your job, your employer will likely cover the costs of the premiums. On the other hand, if you obtain insurance through an association, you will be responsible for the payments.
No matter what, everyone in a group plan has the same essential coverage. But if you buy your health insurance policy, you can choose which features will benefit you most.
Questions to ask about group health insurance in Canada
If your job provides health insurance coverage, you should ask the HR department about plan details. Request a group benefits booklet if you haven't already received one. You should find out when the policy starts and potentially ends.
Determining which insurer supplies your medical insurance is essential. Additionally, inquire if the collective policy provides coverage for pre-existing illnesses. Finally, choosing whether a medical examination is necessary to demonstrate that you are eligible for insurance coverage is important.
Coordinating spousal and dependent supplementary insurance benefits
If your spouse is currently working, take the time to review each other's supplemental health insurance. You must know what is and isn't covered by your plans. This review should include your current dependent coverage, if any.
If you or your spouse are unemployed, most employers offer health insurance for a spouse or dependents. You will likely need to pay the health insurance premium each month. But this is an excellent opportunity to ensure complete family coverage, even if one of you is not working.
Assessing your insurance needs
You might question buying additional health insurance coverage if you are healthy. But, ultimately, buying extra insurance is a deeply individual decision.
Universal health coverage is a great way to care for most medical necessities. But many additional services are not included.
It is not recommended to be in the position of having to pay for medical services not covered by Canadian Medicare. These costs can be very high and difficult to manage, potentially resulting in stress-related health issues.
Insurance and the effects of age
Wondering if age affects the cost of extra health insurance? It is usually much cheaper when you are younger, meaning your premiums will be lower. However, you may have more medical conditions that need attention when you are older, meaning a higher monthly premium.
The insurance company considers younger people less of a liability, and therefore they can offer lower rates for their policies. But they will also consider your lifestyle decisions, such as whether you smoke, how much you drink, and more.
Choosing a supplementary insurance policy
Selecting a supplementary health insurance plan that suits your requirements is essential. You may also consider critical illness insurance to augment your chosen plan.
Creditpicks
Tweet
Consulting a reliable source such as a lawyer or accountant may be beneficial when looking for a health insurance policy. Additionally, seeking advice from your network of family and friends is advisable. You should read the yearly reports of insurance companies to find a suitable insurance plan.
There are numerous ways to acquire health insurance coverage, such as through an employer, an insurance company, or an insurance agent.
Selecting a supplementary health insurance plan that suits your requirements is essential. You may also consider critical illness insurance to augment your chosen plan.
Direct pay or submitting a claim
Most supplementary insurance providers offer a direct payment option for your medical services providers. However, if not, you must know how to submit a claim for medical expenses reimbursement.
Your policy provider likely has an online- and app-based system to submit claims. Contact your insurance company for additional information regarding direct payment and submitting claims.
A general checklist for submitting a medical reimbursement claim
Submitting a medical claim for reimbursement in Canada can involve several steps. The requirements depend on your specific situation and the province you live in. Here's a general checklist to help guide you through the process:
- Determine your eligibility: Ensure you are eligible for medical reimbursement under your province's health care plan, private insurance plan, or both.
- Obtain necessary forms: Collect the required forms for submitting a claim. These may include the following:
- Provincial health care plan forms may vary depending on the province.
- Private insurance claim forms if you have additional coverage through a private insurer.
- Gather documentation: Compile all necessary documentation to support your claim, including:
- Original receipts or invoices for medical services, devices, or prescriptions.
- Medical referral letters, if required.
- Any additional documentation required by your province or private insurer, such as diagnostic reports or treatment plans.
- Fill out claim forms: Complete the required forms with accurate and up-to-date information. Make sure to include the following:
- Personal information, such as name, address, and date of birth.
- Health card number or insurance policy number.
- Details of the medical service, device, or prescription, including dates, provider information, and costs.
- Any necessary supporting documentation.
- Double-check your forms: Review your claim forms and supporting documentation for accuracy and completeness. Ensure you've filled out all necessary sections and included all required attachments.
- Make copies: Make copies of your completed claim forms and supporting documentation for your records.
- Submit your claim: Submit your claim forms and supporting documentation to the appropriate organization. Depending on your province's or private insurer's requirements, you may complete this by mail or electronically. Be sure to follow any specific submission guidelines provided.
- Track your claim: Keep track of the status of your claim and follow up with the appropriate organization if you don't receive a response within the expected time frame.
- Review reimbursement: Once your claim is processed, ensure it meets your expectations. Contact the appropriate organization to inquire about the issue if you believe there are errors or discrepancies.
- Save records: Keep all your claim and reimbursement records for future reference. You may need them for tax purposes or to submit additional claims.
Remember that the steps and requirements for submitting a medical claim for reimbursement may vary. This depends on your province and the details of your private insurance plan. Always consult your province's health care plan and private insurer for the most accurate and up-to-date information.
Questions regarding your coverage?
Insurance can be complicated and difficult to understand. If you have insurance through your employer, you can learn additional details from your HR department. If you want to opt for an individual plan instead, contact your insurance representative or the company itself to learn more.
The policy provider or insurance agent should communicate with you in an easy-to-understand way. It is their job to ensure you can access plan benefits when needed.
Supplementary insurance is part of your financial plan
Supplemental coverage provides a direct counterbalance to the financial impacts of health concerns. While paying into a broader insurance group, this insurance aims to help you remain stress-free while seeking needed treatments. Employers, some associations, and direct insurance normally provide access to supplementary health insurance. You must understand what your plan covers, any premiums, the deductibles and co-insurance, and how to file a claim if direct pay is unavailable.
You should also consider making insurance an integrated part of your bigger financial plan. This insurance might include homeowner's or renter's, auto or car, life, or critical illness and disability coverage. Your goal is to protect yourself and your loved ones in an emergency. And to ensure you get the best care or support during a time of need. If you found this helpful, subscribe to our mailing list to get first access to new posts and updates!




